CPR-Definition
CPR stands for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation. CPR is an emergency lifesaving which is performed when the heart stops beating. Instant CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) might double or triple the probabilities of survival after cardiac arrest.
CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) is a technique used to maintain and restore breathing and circulation and in order to give oxygen and blood flow to the brain, heart and other essential organ. It can be performed by healthcare professionals or trained laypeople on adults, adolescents or infants. It must be performed when an adolescent, adult, infant, or child is not breathing and is unconscious.

Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) is a technique which is used to help and maintain breathing and circulation for adolescent, child or infant who has respiratory arrests and cardiac arrest. The cardiac and respiratory arrest are caused by an ineffective heartbeat, asphyxiation, allergic reactions, breathing passages, which are choking, blocked, drug reactions, drowning etc. In newborns, CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) is caused due to failure of the respiratory, which is caused by SIDS sudden infant death syndrome, drowning, neurologic disease, sepsis.
The CPR procedures differ for adolescents, children and infants. The two organizations which are American Red Cross and American Heart Association that give CPR training and guidelines, distinguish adolescents, children and infants for the CPR’s purpose are as follows:
- Adult comprises children aged eight years or more than eight years.
- Child comprises ages between 1 to 8 years.
- Infant comprises newborns and extends to the age of one year.
About High-Quality CPR
Anyone can perform the high-quality CPR including bystanders. Following are the main components:
- Reduce chest compressions interruptions.
- Give adequate rate and depth compressions.
- Avoid inclined on the victim between compressions
- Guarantee appropriate hand placement
- Avoid extreme ventilation
Chain of Survival
In the AHA’s chain of survival, CPR is an important step. The chain of survival term gives a helpful metaphor for the components of the ECC system concept:
In the adult-out-of-hospital chain of survival, there are 6 links:
- Identification of heart failure and initiation of the emergency response system (In US, calling 9-1-1).
- Initial CPR with an accentuation on chest compressions
- Quick defibrillation
- Progressed revival by Emergency Medical Services and providers of other medical care.
- Post-heart failure care
- Recovery (including extra treatment, psychological support, rehabilitation and observation)
A solid Chain of Survival can improve possibilities of endurance and recovery for victims of heart failure.
What are the Three Parts of CPR?
By using the simple word ‘CAB,’ we can easily remember the basic three parts of the CPR.
- C is for Compressions: – Chest compressions help in the flow of the brain, heart, and different organs. With the 30 chest compressions, CPR starts, followed by two salvage breaths.
- A is for Airway: – Check the airway of a person after 30 compressions in order to ensure that it is open for breathing.
The airway might be blocked by the tongue whenever someone loses consciousness or from food. - B is for relaxing: – After 30 compressions, the rescue breathing starts when the airway is open. Somebody doing rescue breathing relaxes for the victim by compelling air into the lungs. This incorporates breathing into the mouth of the victim at the correct time and checking for indications of life.
CPR Step-by-Step
There are two stages of CPR:
- Preparation Stage
- CPR Stage
1. Preparation Stage
We have to perform the following steps before performing CPR on an adult:
Step1. Call 911
First, we have to check the scene for aspects that may put us in a risk. Like falling masonry, fire, traffic, etc., then we have to check the condition of the person like Do they need support? Tap on their shoulder and shout, “Are you alright”?
If the person is not answering, then we need to call on the number 911 or ask an onlooker to call on the number 911 before performing CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation). If there is a possibility, request that an onlooker proceed to search for an AED machine. Individuals can locate these in workplaces and numerous other public buildings.
Step 2. Place the individual on their back and open their airway
Sensibly, Spot the individual on their back and bow alongside their chest. With their jaws raised, tilt their head back.
Open their mouth and check for any obstacle, for example, food or regurgitation. Eliminate any obstacle then loosen it. When it is not loose then try to hold it might push it farther into the airway.
Step 3. Check for Breathing
Put your ear near to the mouth of the person and listen for close to 10 seconds. In the situation where you do not hear breathing, or you just hear uneven breaths, start CPR.
Do not perform CPR in the situation that an individual is still deprived of breathing. Alternately, place them in the position of recovery if they do not suffer spinal cord injury. Continue observing their breathing, and whenever they stop breathing, then performing CPR.
CPR Steps
There are various steps to perform Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR):
Step 4. Perform 30 Chest Compressions
Spot one hand on top of the other and hold them together. With the impact point of the hands and straight elbows, push fast and hard in the chest’s center, marginally underneath the nipples. At least 2 inches deep, we have to push. At a rate of at least 100 times per minute, we need to compress their chest. Allow the chest to fully lift between compressions.

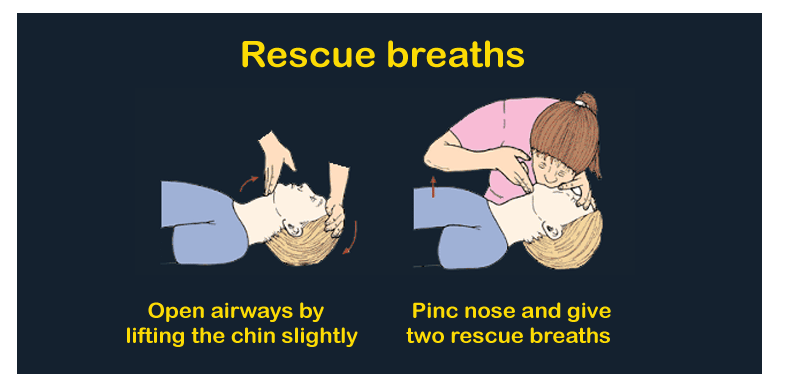
Step 5. Perform two rescue breaths
While making sure that their mouth is clean, tilt their head back somewhat and raise their chin. Close their nostrils, place your mouths totally over their mouth, and jerk their chest up.
If with the first breath, their chest does not lift, then retract their head. If the individual still does not lift his chest with a second breath then he may suffocate.
Step 6. Repeat
Repeat this process of two rescues breathes and 30 chest compressions until the individual begin breathing or support arrives. In the situation that an AED arrives, continue doing CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) until the machine is set up and prepared to utilize.
