File Operations in Java
In Java, a File is an abstract data type. A named location used to store related information is known as a File. There are several File Operations like creating a new File, getting information about File, writing into a File, reading from a File and deleting a File.
Before understanding the File operations, it is required that we should have knowledge of Stream and File methods. If you have knowledge about both of them, you can skip it.
Stream
A series of data is referred to as a stream. In Java, Stream is classified into two types, i.e., Byte Stream and Character Stream.

Byte Stream
Byte Stream is mainly involved with byte data. A file handling process with a byte stream is a process in which an input is provided and executed with the byte data.
Character Stream
Character Stream is mainly involved with character data. A file handling process with a character stream is a process in which an input is provided and executed with the character data.
To get more knowledge about the stream, click here.
Java File Class Methods
| S.No. | Method | Return Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | canRead() | Boolean | The canRead() method is used to check whether we can read the data of the file or not. |
| 2. | createNewFile() | Boolean | The createNewFile() method is used to create a new empty file. |
| 3. | canWrite() | Boolean | The canWrite() method is used to check whether we can write the data into the file or not. |
| 4. | exists() | Boolean | The exists() method is used to check whether the specified file is present or not. |
| 5. | delete() | Boolean | The delete() method is used to delete a file. |
| 6. | getName() | String | The getName() method is used to find the file name. |
| 7. | getAbsolutePath() | String | The getAbsolutePath() method is used to get the absolute pathname of the file. |
| 8. | length() | Long | The length() method is used to get the size of the file in bytes. |
| 9. | list() | String[] | The list() method is used to get an array of the files available in the directory. |
| 10. | mkdir() | Boolean | The mkdir() method is used for creating a new directory. |
File Operations
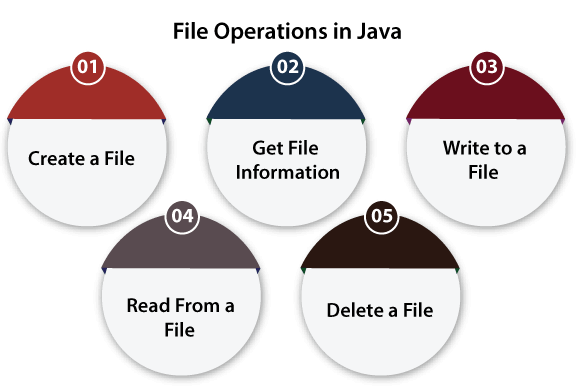
We can perform the following operation on a file:
- Create a File
- Get File Information
- Write to a File
- Read from a File
- Delete a File
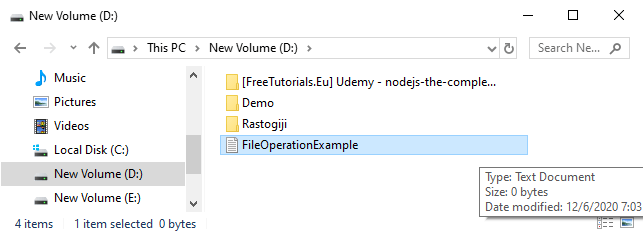
Create a File
Create a File operation is performed to create a new file. We use the createNewFile() method of file. The createNewFile() method returns true when it successfully creates a new file and returns false when the file already exists.
Let’s take an example of creating a file to understand how we can use the createNewFile() method to perform this operation.
CreateFile.java
Output:

Explanation:
In the above code, we import the File and IOException class for performing file operation and handling errors, respectively. We create the f0 object of the File class and specify the location of the directory where we want to create a file. In the try block, we call the createNewFile() method through the f0 object to create a new file in the specified location. If the method returns false, it will jump to the else section. If there is any error, it gets handled in the catch block.
Get File Information
The operation is performed to get the file information. We use several methods to get the information about the file like name, absolute path, is readable, is writable and length.
Let’s take an example to understand how to use file methods to get the information of the file.
FileInfo.java
Output:

Description:
In the above code, we import the java.io.File package and create a class FileInfo. In the main method, we create an object of the text file which we have created in our previous example. We check the existence of the file using a conditional statement, and if it is present, we get the following information about that file:
- We get the name of the file using the getName()
- We get the absolute path of the file using the getAbsolutePath() method of the file.
- We check whether we can write data into a file or not using the canWrite()
- We check whether we can read the data of the file or not using the canRead()
- We get the length of the file by using the length()
If the file doesn’t exist, we show a custom message.
Write to a File
The next operation which we can perform on a file is “writing into a file”. In order to write data into a file, we will use the FileWriter class and its write() method together. We need to close the stream using the close() method to retrieve the allocated resources.
Let’s take an example to understand how we can write data into a file.
WriteToFile.java
Output:

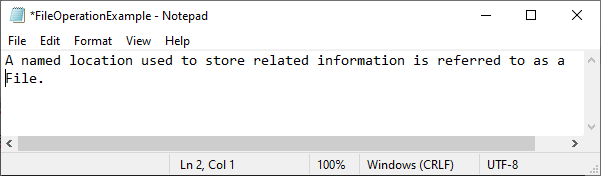
Explanation:
In the above code, we import the java.io.FileWriter and java.io.IOException classes. We create a class WriteToFile, and in its main method, we use the try-catch block. In the try section, we create an instance of the FileWriter class, i.e., fwrite. We call the write method of the FileWriter class and pass the content to that function which we want to write. After that, we call the close() method of the FileWriter class to close the file stream. After writing the content and closing the stream, we print a custom message.
If we get any error in the try section, it jumps to the catch block. In the catch block, we handle the IOException and print a custom message.
Read from a File
The next operation which we can perform on a file is “read from a file”. In order to write data into a file, we will use the Scanner class. Here, we need to close the stream using the close() method. We will create an instance of the Scanner class and use the hasNextLine() method nextLine() method to get data from the file.
Let’s take an example to understand how we can read data from a file.
ReadFromFile.java
Output:

Expalnation:
In the above code, we import the “java.util.Scannner”, “java.io.File” and “java.io.IOException” classes. We create a class ReadFromFile, and in its main method, we use the try-catch block. In the try section, we create an instance of both the Scanner and the File classes. We pass the File class object to the Scanner class object and then iterate the scanner class object using the “While” loop and print each line of the file. We also need to close the scanner class object, so we use the close() function. If we get any error in the try section, it jumps to the catch block. In the catch block, we handle the IOException and print a custom message.
Delete a File
The next operation which we can perform on a file is “deleting a file”. In order to delete a file, we will use the delete() method of the file. We don’t need to close the stream using the close() method because for deleting a file, we neither use the FileWriter class nor the Scanner class.
Let’s take an example to understand how we can write data into a file.
DeleteFile.java
Output:

Explanation:
In the above code, we import the File class and create a class DeleteFile. In the main() method of the class, we create f0 object of the file which we want to delete. In the if statement, we call the delete() method of the file using the f0 object. If the delete() method returns true, we print the success custom message. Otherwise, it jumps to the else section where we print the unsuccessful custom message.
All the above-mentioned operations are used to read, write, delete, and create file programmatically.
