General Annotations in Jackson
General annotations include several basic annotations which we use in serialization and deserialization. JsonProperty and JsonView are the two generally used annotations at the time of serialization and deserialization.

Let’s understand each one of them in detail with an example:
@JsonProperty
It is an important general annotation that we used for marking the non-standard getter/setter method, i.e., to be used with respect to Json Property. Let’s take an example to understand how it works:
JsonPropertyExample.java
Output:

@JsonFormat
It is another important annotation that is used for specifying the format at the time of serialization and deserialization. It is mostly used for specifying date format.
Let’s take an example to understand how annotation is used for specifying a format for the date field.
JsonFormatExample.java
Output:

@JsonUnwrapped
It is another important annotation that comes in general annotations. It is used for unwrapping an object’s values at the time or serialization and deserialization.
Let’s take an example to understand how the annotation is used for wrapping the values.
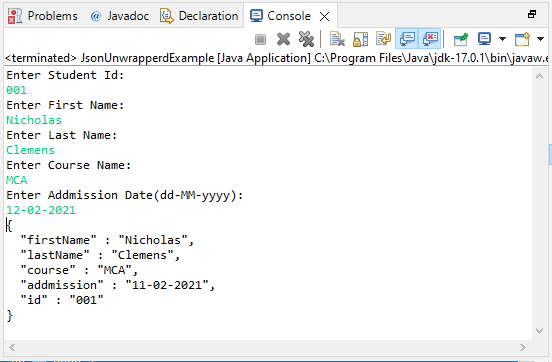
JsonUnwrapperdExample.java
Output:
@JsonUnwrapped
It is another important annotation that is used for controlling values to be serialized or not. Let’s take an example to understand how the annotation is used for controlling the values.
JsonViewExample.java
Output:

@JsonManagedReferences/@JsonBackReferences
@JsonManagedReference and @JsonBackReferences are the two important annotations that are used for displaying the relationship with the parent-child relationship.
@JsonManagedReference is used for referring to parent objects whereas @JsonBackReferences is used for marking child objects.
Let’s take an example to understand how both annotations are used for displaying relationship between objects.
JsonReferenceExample.java
Output:

@JsonIdentityInfo
When objects have a parent-child relationship, @JsonIdentityInfo is used for indicating that object identity will be used during serialization/deserialization.
Let’s take an example to understand the working of @JsonIdentityInfo annotation.
JsonIdentityInfoExample.java
Output:

@JsonFilter
@JsonFilter is another useful annotation that we used for applying filters at the time of serialization/deserialization.
Let’s take an example to understand how we can apply filters by using @JsonFilter.
JsonFilterExample.java
Output:

