The Jarque-Bera test is a goodness-of-fit test that determines whether or not sample data have skewness and kurtosis that matches a normal distribution.
The test statistic of the Jarque-Bera test is always a positive number and if it’s far from zero, it indicates that the sample data do not have a normal distribution.
The test statistic JB is defined as:
JB =(n/6) * (S2 + (C2/4))
where:
- n: the number of observations in the sample
- S: the sample skewness
- C: the sample kurtosis
Under the null hypothesis of normality, JB ~ X2(2)
This tutorial explains how to conduct a Jarque-Bera test in Excel.
Jarque-Bera test in Excel
Use the following steps to perform a Jarque-Bera test for a given dataset in Excel.
Step 1: Input the data.
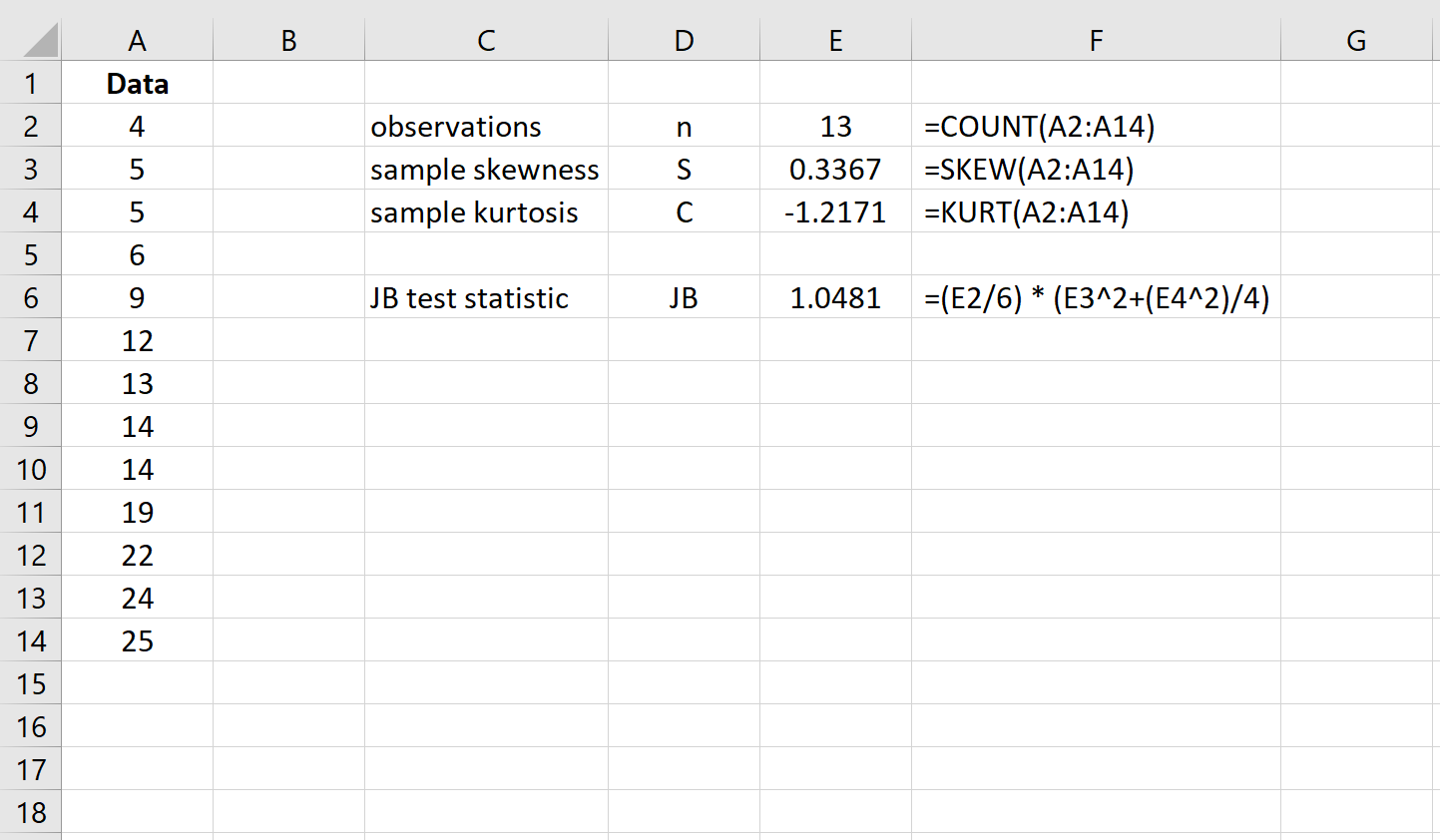
First, input the dataset into one column:

Step 2: Calculate the Jarque-Bera Test Statistic.
Next, calculate the JB test statistic. Column F shows the formulas used:
Step 3: Calculate the p-value of the test.
Recall that under the null hypothesis of normality, the test statistic JB follows a Chi-Square distribution with 2 degrees of freedom. Thus, to find the p-value for the test we will use the following function in Excel: =CHISQ.DIST.RT(JB test statistic, 2)
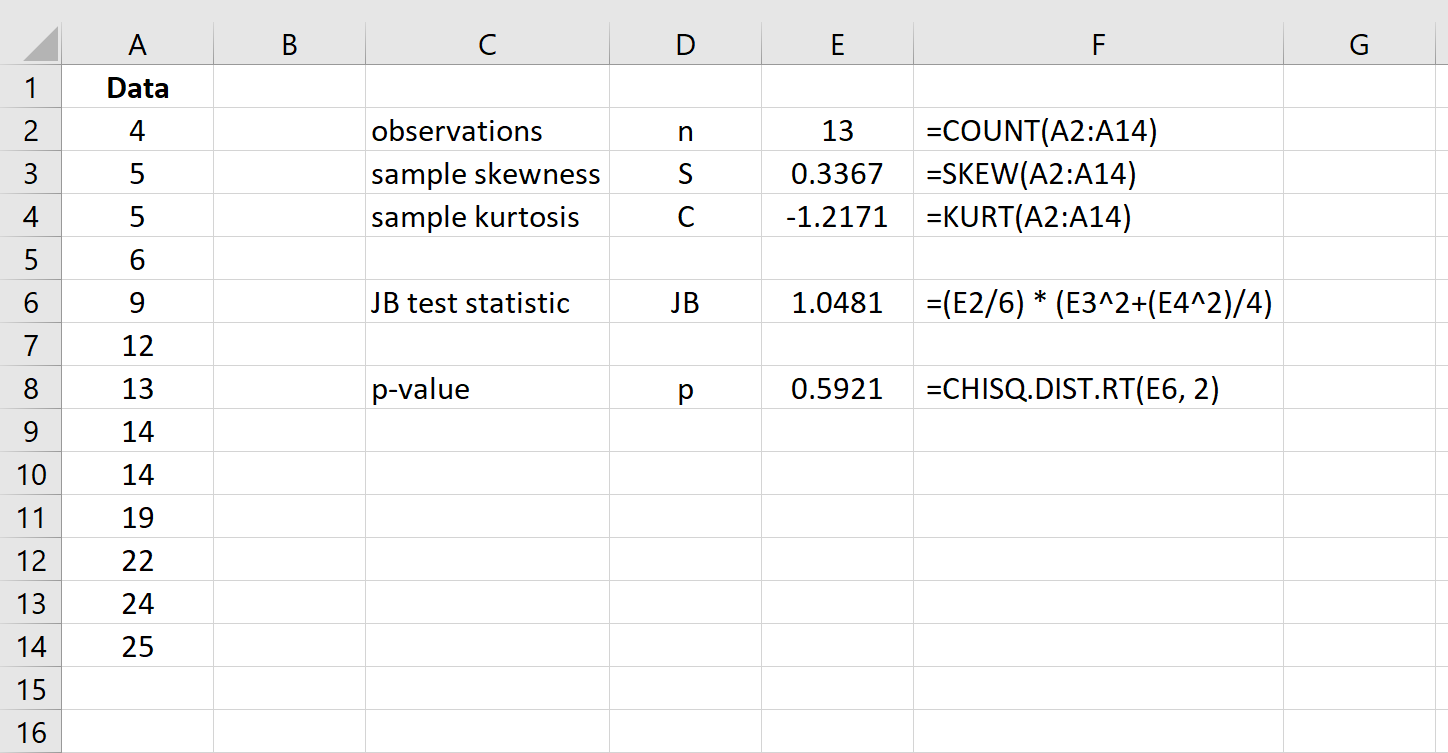
The p-value of the test is 0.5921. Since this p-value is not less than 0.05, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. We don’t have sufficient evidence to say that the dataset is not normally distributed.
