Largest Cell in Human Body
The ovum, also known as the egg cell, is the female body’s reproductive cell. The human egg (ovum) is the body’s largest cell, while a nerve cell is the body’s longest cell. According to most scientists, the sperm cell is the tiniest and most complex cell in the human body. The head of a sperm cell is roughly 4 micrometer’s long, about the same size as a red blood cell (RBCs).
The ovum is 20 times the size of sperm cells, with a diameter of roughly 0.1 mm. Each ovum is fenced by a hollow clump of cells termed as follicle. The ovum matures within the follicle throughout time. Once a follicle is stimulated, it takes around four months to develop. Some follicles remain latent for forty years before maturing, while others deteriorate and never mature. During the child-bearing period, 300 to 400 follicles develop and produce fertile eggs. Most of a woman’s remaining follicles get deteriorated by the time she reaches menopause.
What is Ovum?
The Latin term ovum means ‘egg,’ and the plural form of ovum is ova. The women’s reproductive haploid gamete is known as an ovum. Animals and terrestrial plants, such as embryophytes, both produce ova. The meaning of ovum was originally specified in 1672. A sole cell produced from either of the female reproductive organs, the ovaries, when impregnated (combined) with a sperm cell is capable of growing into a new life. A stratum of cells (germinal epithelium) covers the external surface of every ovary, which surrounds the young egg cells that are present in the ovaries from birth.
Make-up of Human Ovum
The human ovum has a mi?role?ith?l anatomy with a lot of ?yt??l?sm. The cyt??l?sm is divided into two sections:
- The outer: smaller, and transparent ex??l?sm, or egg cortex
- and The inner: larger, and opaque end??l?sm, or o??l?sm.
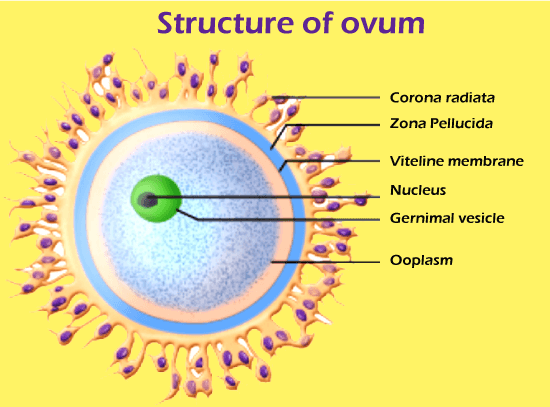
Microtubules and microfilament’s, pigment granules, and corti??l granules of mu??-??lys?cch?rides are some of the cytoskeletal structures seen in the egg cortex. End??l?sm involves cell organelles, inf?rm?somes, tRNAs, histones, enzymes, and other components. The germinal vesicle is a large nucleus of the ovum that is bloated with nucleoplasm. Because the nucleus is exocentric in its position, the human ovum has a polarity. The animal pole is the side of the ovum with the nucleus and polar body, while the vegetal pole is the side with the ????site. A vitelline membrane, zona pellucida, and corona radiata are some of the egg envelopes that enclose the structure of the egg envelope. The thick cell wall (vitelline membrane) is a thin, translucent inner membrane. It is produced by the ovum themselves. The middle zone is pellucida, which is thin, translucent, and non-cellular. They are secreted in part by follicular cells and oocytes.
Functions of ovum
The ovum’s primary role is to transport the chromosomes provided by the female gamete. It creates the ideal conditions for fertilization to take place. It also supplies nutrition to the developing embryo until it settles into the uterus and the placenta takes control. The nucleus of the ovum contains the genetic material of the female. The traits of the child inherited are determined by the female genetic material and the sperm cell. The nucleus is encircled by the cell plasma or yolk, which holds the nutrients required for the egg cell’s development.
