You can use the rand() function in SAS to generate random numbers.
The following examples show how to use this function in practice.
Example 1: Generate One Random Number
The following code shows how to generate a single random integer in SAS between 1 and 10:
/*create dataset with variable that contain random value*/
data my_data;
call streaminit(1); /*make this example reproducible*/
x = rand("integer", 1, 10);
output;
run;
/*view dataset*/
proc print data=my_data;

The random number between 1 and 10 turned out to be 9.
Note that we used the streaminit() function to ensure that this example is reproducible. This means that each time we run this code, the random number will be 9.
Feel free to leave out the streaminit() function to produce a different random value each time you run the code.
Example 2: Generate Variable with Several Random Numbers
The following code shows how to generate a variable in SAS that contains 10 random values between 1 and 20:
/*create dataset with variable that contain random value*/
data my_data;
call streaminit(10);
do i = 1 to 10;
x = rand("integer", 1, 20);
output;
end;
run;
/*view dataset*/
proc print data=my_data; 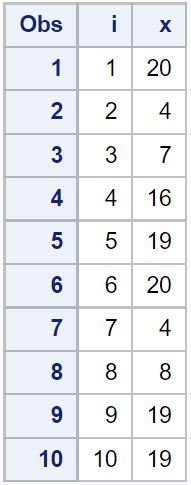
Notice that each of the values for the variable x are random integers between 1 and 20.
Example 3: Generate Multiple Variables with Several Random Numbers
The following code shows how to generate multiple variables in SAS that contain random values:
/*create dataset with variable that contain random value*/
data my_data;
call streaminit(10);
do i = 1 to 10;
x = rand("integer", 1, 20);
y = rand("integer", 50, 100);
output;
end;
run;
/*view dataset*/
proc print data=my_data; 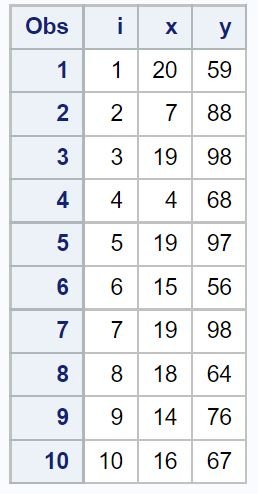
The x variable contains 10 random integers between 1 and 20 while the y variable contains 10 random integers between 50 and 100.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in SAS:
How to Normalize Data in SAS
How to Rename Variables in SAS
How to Remove Duplicates in SAS
How to Replace Missing Values with Zero in SAS
