Types of Statements in Java
Statements are roughly equivalent to sentences in natural languages. In general, statements are just like English sentences that make valid sense. In this section, we will discuss what is a statement in Java and the types of statements in Java.
What is statement in Java?
In Java, a statement is an executable instruction that tells the compiler what to perform. It forms a complete command to be executed and can include one or more expressions. A sentence forms a complete idea that can include one or more clauses.
Types of Statements
Java statements can be broadly classified into the following categories:
- Expression Statements
- Declaration Statements
- Control Statements
Expression Statements
Expression is an essential building block of any Java program. Generally, it is used to generate a new value. Sometimes, we can also assign a value to a variable. In Java, expression is the combination of values, variables, operators, and method calls.
There are three types of expressions in Java:
- Expressions that produce a value. For example, (6+9), (9%2), (pi*radius) + 2. Note that the expression enclosed in the parentheses will be evaluate first, after that rest of the expression.
- Expressions that assign a value. For example, number = 90, pi = 3.14.
- Expression that neither produces any result nor assigns a value. For example, increment or decrement a value by using increment or decrement operator respectively, method invocation, etc. These expressions modify the value of a variable or state (memory) of a program. For example, count++, int sum = a + b; The expression changes only the value of the variable sum. The value of variables a and b do not change, so it is also a side effect.
Declaration Statements
In declaration statements, we declare variables and constants by specifying their data type and name. A variable holds a value that is going to use in the Java program. For example:
Also, we can initialize a value to a variable. For example:
Java also allows us to declare multiple variables in a single declaration statement. Note that all the variables must be of the same data type.
Control Statement
Control statements decide the flow (order or sequence of execution of statements) of a Java program. In Java, statements are parsed from top to bottom. Therefore, using the control flow statements can interrupt a particular section of a program based on a certain condition.
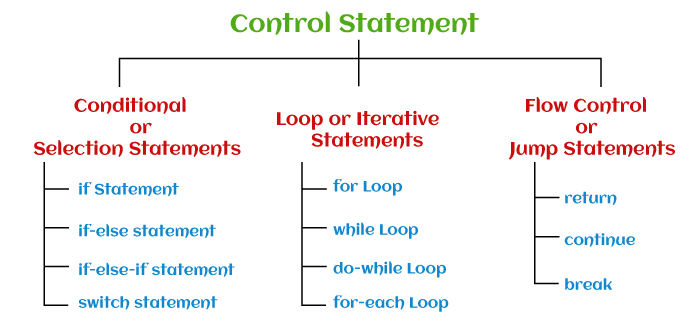
There are the following types of control statements:
- Conditional or Selection Statements
- Loop or Iterative Statements
- Flow Control or Jump Statements
Example of Statement
